Research Shows Clinton Loss Is More Complex Than a Simple Urban-Rural Divide

Although Democrat Hillary Clinton won the popular vote by nearly 3 million, she still lost the 2016 presidential election to Republican Donald Trump. A closer look into the votes cast reveals that one of the factors of Clinton’s loss could be attributed to her underperformance in rural areas. New research suggests that while she nearly matched Barack Obama’s 2012 performance in most urban areas, she failed to match the Democratic presidential nominees in the last five elections in the less populated areas of the country.
The research was released this week by the Carsey School of Public Policy at the University of New Hampshire and was conducted by Dante Scala — associate professor of political science and a faculty fellow at the Carsey School — and Kenneth Johnson, senior demographer at the Carsey School and professor of sociology.
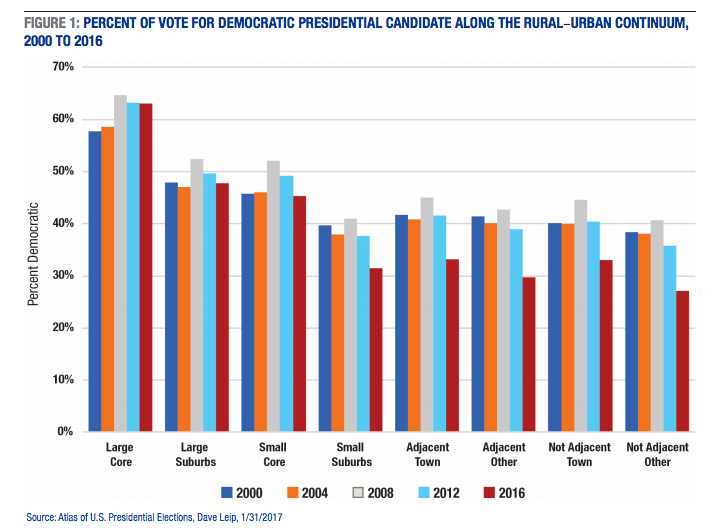
The researchers examined voting along a rural to urban continuum, rather than treating rural and urban as a polarity. They found significant variations in voting behavior among both urban and rural places that persist over the last five presidential elections.
“Yet, defining 2016 as the tale of two Americas — one urban, one rural — hinders a nuanced understanding of the country’s political geography,” the researchers stated. “Many political commentators mistakenly caricature rural America as a single entity, but our research … shows that complex variations in voting patterns persist among both urban and rural places.”
Several headlines after the election pushed the urban-rural divide that existed in the election. “How the Election Revealed the Divide Between City and Country,” read a piece by The Atlantic. The researches suggest that while the overall premise is true, it’s a lot more complicated than that because political pundits don’t often include suburban voters or towns adjacent to suburbs.
Clinton received 2.1 million fewer votes in rural America than Obama did four years earlier even though 531,000 more votes were cast there in 2016. Large urban counties are the base of the Democratic Party as well as their suburbs and the cores of smaller metropolitan areas. The outer edges of smaller urban areas and the vast rural regions tend to be Republican territory.
“Through the last five presidential elections voting patterns were consistent along a rural-urban continuum,” the researchers said. “Democrats did best at the urban end of the continuum and Republicans at the rural end. What is distinctly different in 2016 is that Hillary Clinton did far worse across the entire rural end of the continuum than any Democratic candidate in the previous four presidential elections.”
At one end of the continuum are the urban core counties of large metropolitan areas. This is where Democrats have received their greatest support in the last five presidential elections. Al Gore and John Kerry averaged slightly less than 60 percent of the vote in these areas in 2000 and 2004. Barack Obama boosted the Democrats’ urban vote share in 2008 and 2012, and Clinton maintained it in 2016. Also, the suburbs of these large metropolitan areas gave both Obama in 2012 and Clinton slightly less than a majority (49.6 and 47.8 percent, respectively).
Next on the continuum, the suburbs of smaller urban areas are more strongly Republican. It is at this point on the rural–urban continuum that the contrast between earlier elections and 2016 is evident. Here the gap between Democratic support in 2012 and 2016 widened, which ultimately led to Clinton’s loss.
At the rural end of the continuum, counties tend to be more Republican, but there is variation within these rural areas. Democrats consistently did worse in counties remote from urban areas, and in those without large towns of 10,000 to 50,000 people. This pattern continued in 2016, but there was a substantial decline in support for Clinton across all types of rural counties. For example, in 2012, Obama received 41.6 percent of the vote in rural counties adjacent to metropolitan areas that contained a large town and 38.9 percent in those that did not. Clinton received just 33.1 percent in these adjacent large town counties and 29.7 percent in other adjacent counties.
“Certainly, these rural vote totals are dwarfed by those in urban areas. But, from the suburban periphery of smaller urban areas to the most far-flung rural areas, Clinton’s inability to match the performance of any Democratic candidate since at least 2000 contributed to her defeat in crucial swing states such as Florida, Michigan, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin,” the researchers said. “Though many commentators argued that the faster population growth and growing diversity on the urban side of the rural-urban continuum would give Democrats a significant advantage in 2016, the election demonstrated that what happens at the rural end of the continuum remains important.”
Sign up for NH Journal’s must-read morning political newsletter.